Stroke
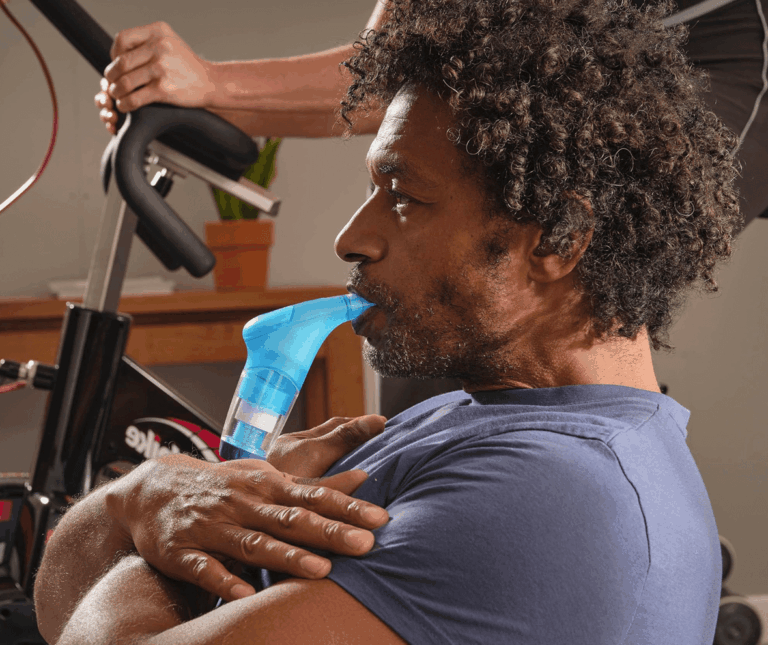
Inspiratory Muscle Training and Expiratory Muscle Training significantly improve your breathing strength, as well as, how well your lungs work in helping you to breathe.

Effect Of Breathing Fatigue In Stroke Recovery
Not only does stroke affect you psychologically and cognitively, but physically too. One aspect of stroke is the feeling of extreme tiredness, or post-stroke fatigue, making movement feel harder and requiring more energy leading to a reduction in tolerance to exercise.
Respiratory muscle strength is impaired after stroke and respiratory weakness will cause dyspnea (shortness of breath), contributing to post-stroke fatigue. The good news is that research shows Respiratory Muscle Training (RMT) to be effective at improving exercise tolerance post-stroke as it improves respiratory function and inspiratory muscle strength which are important when being physically active, exercising, and during rehabilitation sessions.

Reduce Breathing Fatigue And Improve Recovery Post-Stroke
Respiratory muscle training can improve inspiratory muscle strength and POWERbreathe Inspiratory Muscle Training (IMT) is scientifically proven to improve breathing muscle strength, stamina and reduce breathing fatigue.
In fact, this review considers IMT (a component of RMT) to be effective for improving pulmonary function and cardiopulmonary endurance, as well as, reducing pulmonary infection incidence in patients after stroke. Another study finds inspiratory muscle training improves inspiratory function in chronic stroke patients. And this further study shows improvements in exercise capacity, sensation of dyspnoea and quality of life in the IMT group.
When studying respiratory muscle training in stroke patients with respiratory muscle weakness, dysphagia, and dysarthria, this trial finds that Inspiratory Muscle Training with IMT, along with Expiratory Muscle Training with EMT, significantly improves respiratory muscle strength, forced vital capacity, forced expiratory volume per second, and fatigue in stroke patients with respiratory muscle weakness. They also found that training the breathing muscles in this way enhances the improvement in post-stroke dysphagia and dysarthria, concluding that 6-weeks of inspiratory and expiratory training is a helpful therapy in stroke patients.
Researchers also find that people who’ve had a cerebrovascular accident have weak respiratory muscles and are at greater risk of associated pneumonias. However, non-pharmacologic treatment, including breathing techniques, and therapeutic exercise training help to improve the effectiveness of a cough and prevent stroke-associated pneumonia.
Research also recommends that the physical therapist must take into consideration Inspiratory Muscle Training, such as POWERbreathe IMT, for improving physical function in stroke patients.
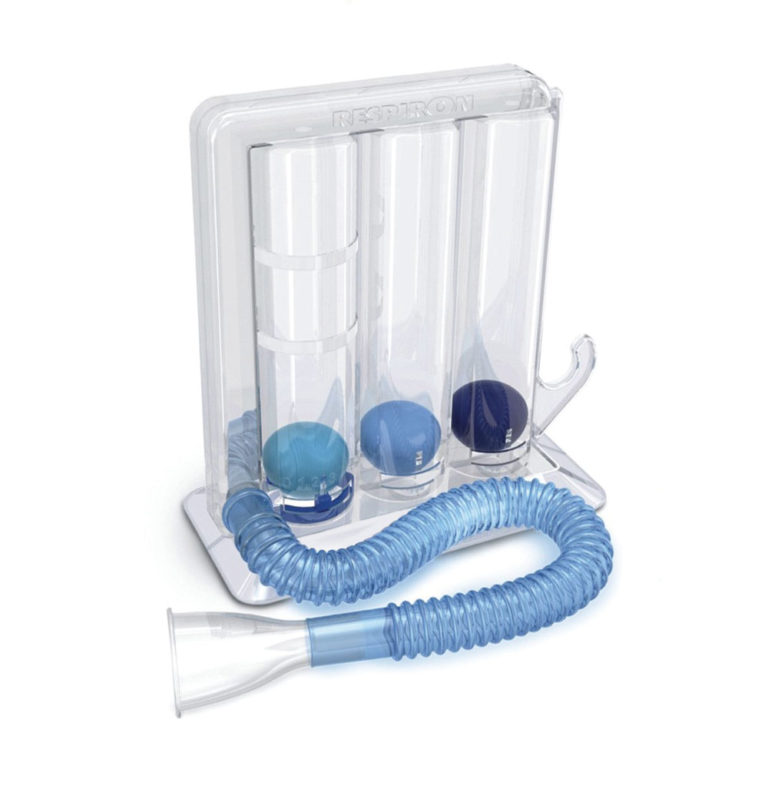
Another technique for improving lung expansion and pulmonary ventilation, although not strength, which is often compromised in stroke patients, is incentive spirometry.